- Introduction
- Configuring checks
- Configuring notifications
- Projects and teams
- Badges
- Pinging API
- Management API
- Reliability Tips
- Shell scripts
- Python
- Ruby
- PHP
- Go
- C#
- Javascript
- PowerShell
- Monitoring cron jobs
- Signaling failures
- Measuring script run time
- Attaching logs
- Cloning checks
- Configuring Prometheus
- Third-party resources
- Overview
- Configuration
- Running with Docker
- Cron syntax cheatsheet
Measuring Script Run Time
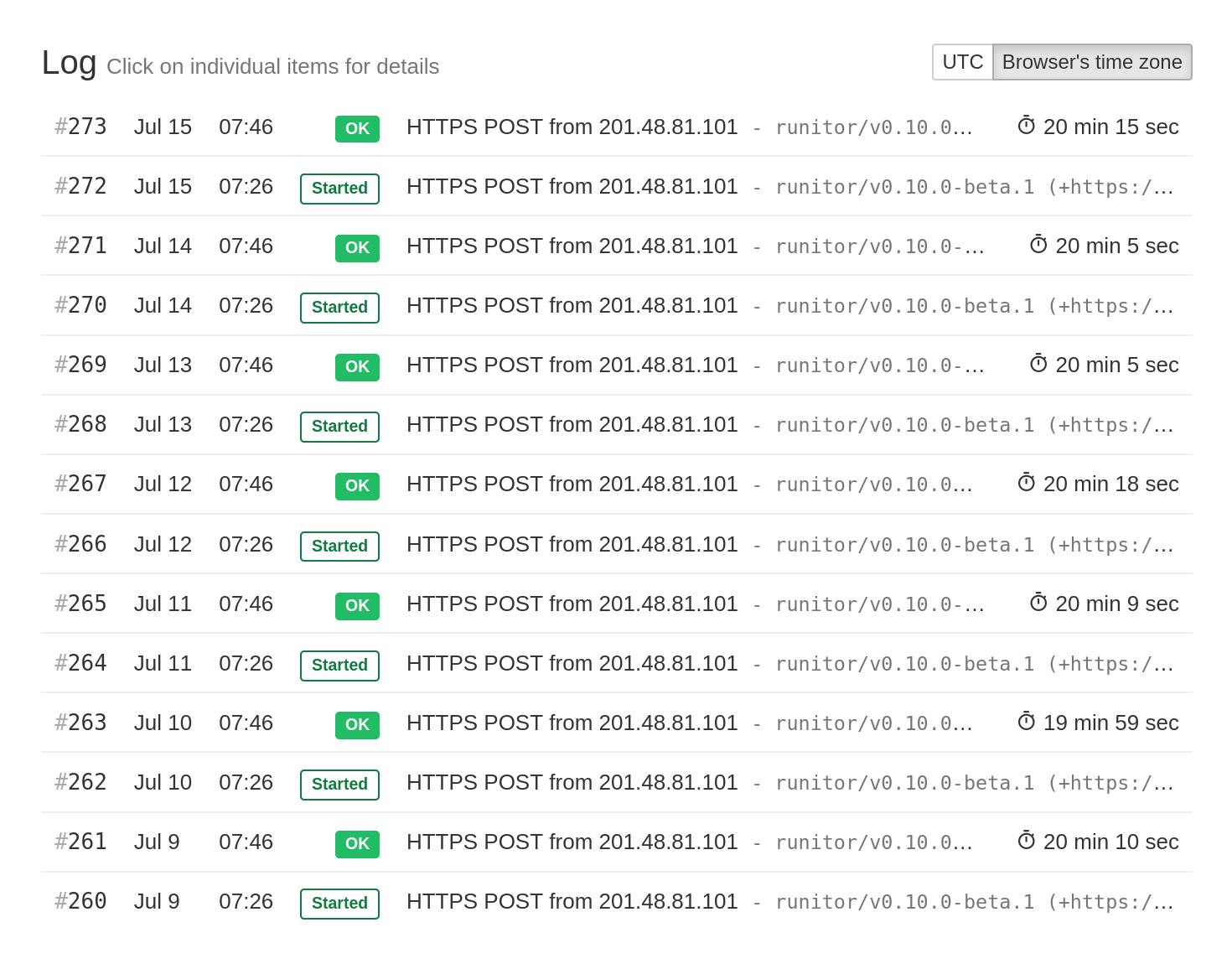
Append /start to a ping URL and use it to signal when a job starts.
After receiving a start signal, Healthchecks.io will show the check as "Started."
It will store the "start" events and display the job execution times. FFT Healthchecks
calculates the job execution times as the time gaps between adjacent "start" and
"success" events.
Alerting Logic
FFT Healthchecks applies an additional alerting rule for jobs that use the /start signal.
If a job sends a "start" signal, but then does not send a "success" signal within its configured grace time, FFT Healthchecks will assume the job has failed. It will mark the job as "down" and send out alerts.
Usage Example
Below is a code example in Python:
import requests
URL = "https://healthchecks.fullfatthings.com/ping/your-uuid-here"
# "/start" kicks off a timer: if the job takes longer than
# the configured grace time, the check will be marked as "down"
try:
requests.get(URL + "/start", timeout=5)
except requests.exceptions.RequestException:
# If the network request fails for any reason, we don't want
# it to prevent the main job from running
pass
# TODO: run the job here
fib = lambda n: n if n < 2 else fib(n - 1) + fib(n - 2)
print("F(42) = %d" % fib(42))
# Signal success:
requests.get(URL)
Viewing Measured Run Times
When FFT Healthchecks receives a "start" signal followed by a regular ping or a "fail" signal, and the two events are less than 72 hours apart, you will see the time delta displayed in the list of checks. If the two events are more than 72 hours apart, they are assumed to be unrelated, and the time delta is not displayed.
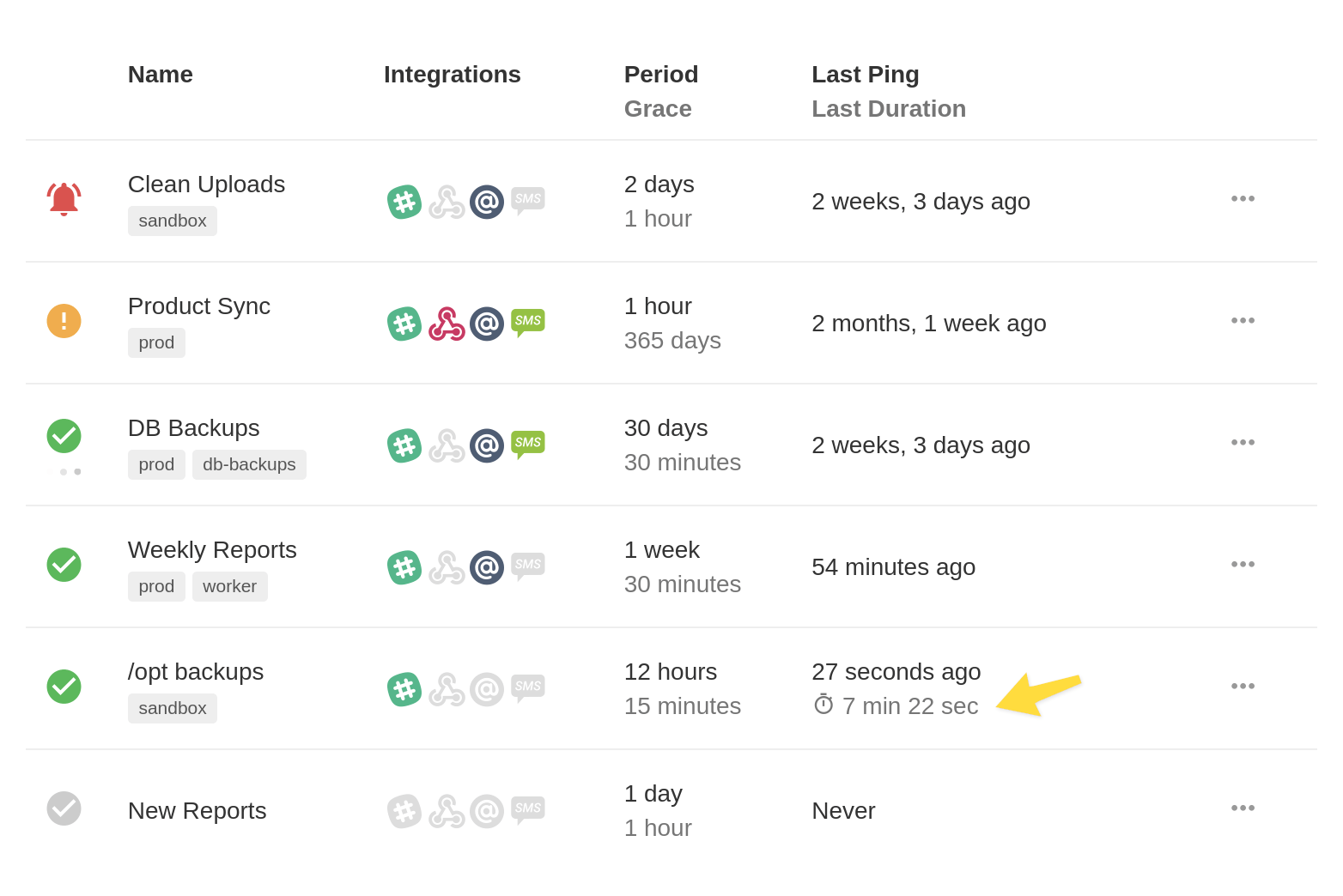
You can also see durations of the previous runs when viewing an individual check: